SLS 3D Printing Service
Unleash unlimited design possibilities with SLS 3D printing, enabling you to easily create complex structures and high-strength parts. No supports needed, offering greater design freedom. The durable materials deliver excellent performance, ideal for functional testing and end-use applications. Fast batch production shortens product development cycles, bringing your innovations to life quickly. Choose SLS for high-quality, high-performance industrial-grade printing solutions!
- High Precision · High Strength · Support-Free
- Excellent mechanical properties and durability.
- Fast batch production, shortening product time-to-market.
Overview of SLS 3D Printing
What is SLS 3D Pringting?
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is an advanced additive manufacturing process that utilizes lasers to selectively fuse powdered materials, typically nylon or other polymers, into solid objects, layer by layer. This technology excels at producing highly complex and intricate parts with exceptional accuracy and fine detail, all without the need for support structures. By sintering the powder material with precision, SLS enables the creation of geometrically complex components that are challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.

How SLS Works
Powder Layering:
A thin layer of powdered material (typically nylon, but can also include other thermoplastics or composites) is spread across the build platform of the 3D printer.
Laser Sintering:
A laser beam selectively scans the surface of the powder, following the design of the part being printed. The laser heats the powder just below its melting point, causing the particles to fuse together (a process known as “sintering”).
Layer-by-Layer Construction:
After a layer is completed, the build platform lowers slightly, and a new layer of powder is applied. The process repeats, with the laser fusing each new layer to the one below it, building the part from the bottom up.
Cooling and Post-Processing:
Once the printing is complete, the entire build chamber needs to cool down. The finished part is then removed from the powder bed, cleaned, and may undergo additional post-processing (e.g., polishing, dyeing, or coating).
ProtoTi SLS 3D Printing Capabilities
Name
Min. Wall Thickness
Max. Build Size
Tolerance
Support Structures
Lead time
Selective Laser Sintering
0.8 mm
360 x 360 x 500 mm
±0.2 mm
No
from 3 business days
SLS 3D Printing Parts Using Various Materials

SLS Nylon PA12
Nylon PA12 is a high-performance polymer widely used in 3D printing, particularly for parts that require strength, wear resistance, and flexibility. It offers excellent chemical stability, high-temperature resistance, and impact resistance, making it ideal for industrial-grade functional components. Due to its low moisture absorption, PA12 maintains stable performance in humid environments and has a smooth surface that can achieve better accuracy and appearance through post-processing.
Key Features:
High strength and toughness
Excellent wear resistance and impact resistance
Superior chemical and thermal stability
Suitable for high-precision printing of complex structures
Good surface finish capabilities
SLS Nylon PA11
Nylon PA11 is a high-performance polymer made from renewable plant sources (such as castor oil), widely used in 3D printing, especially for industrial parts requiring high strength, wear resistance, and flexibility. Compared to PA12, PA11 offers better elasticity and toughness, along with excellent impact resistance and chemical resistance. Its low moisture absorption allows PA11 to maintain good mechanical properties even in humid environments, making it ideal for manufacturing complex structures and functional components.
Key Features:
Excellent strength and toughness
Outstanding wear resistance and impact resistance
Good chemical and thermal stability
Superior elasticity, suitable for flexible parts
Surface finish can be improved through post-processing
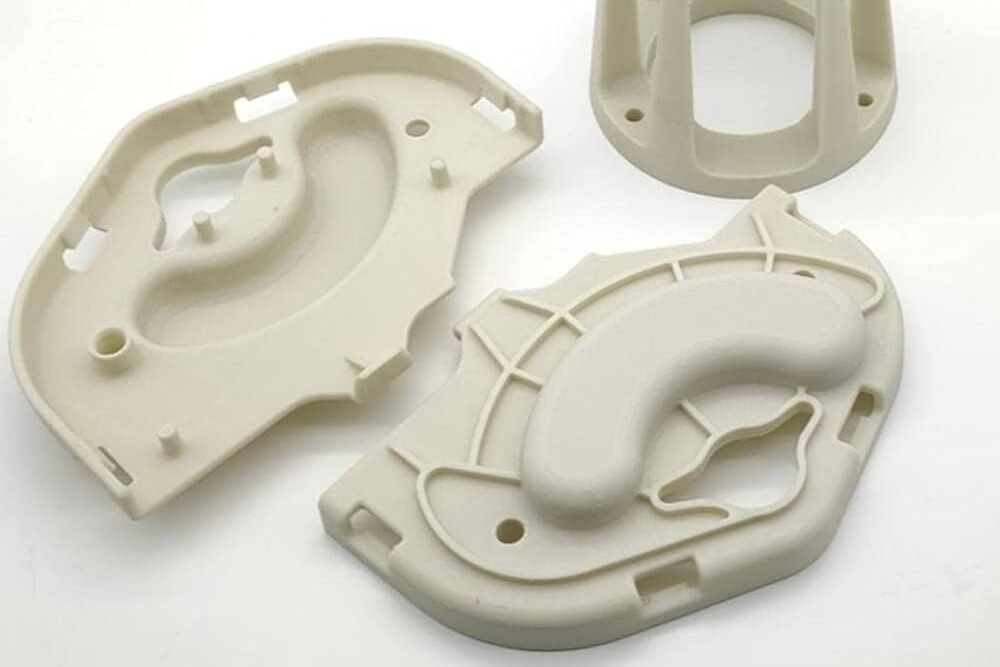

SLS PA12 with Fiberglass
Nylon PA12 with fiberglass is a composite material where glass fibers are added to standard nylon to enhance its strength, rigidity, and heat resistance. The fiberglass-reinforced nylon offers improved mechanical properties and effectively reduces warping and deformation, making it ideal for parts that require high load-bearing capacity and stability. This material is widely used in high-demand applications such as automotive components, industrial tools, and aerospace parts.
Key Features:
Enhanced strength and rigidity, suitable for high load-bearing applications
High temperature resistance and excellent wear resistance, ideal for harsh environments
Strong impact resistance, improving part durability
Low warpage, suitable for printing complex geometries
Improved dimensional stability, ensuring accuracy
SLS 3D Printing Material Specifications
Material Name
Description
Max. Build Size
Elongation at Break (%)
Flexural Strength (MPa)
HDT@0.46 MPa (°C)
Nylon PA12
Solid White,Solid Black,Dyed Black
360 x 360 x 500 mm
10%
52 MPa
120℃
Nylon PA11
Solid Black,Dyed Black
360 x 360 x 500 mm
30%
60 MPa
80℃
SLS PA12 with Fiberglass
Solid White(with yellow),Solid Black,Dyed Black
380 x 380 x 420 mm
5%
100 MPa
150℃
SLS 3D Printing PROS & CONS
Pros
No Support Structure Required:
Because the powder itself can support the printed parts, complex geometries and internal cavities can be directly printed without the need for additional support structures.
High Material Utilization:
Unsintered powder can be reused, reducing waste and lowering material costs.
Good Mechanical Properties:
The printed parts have strength and toughness close to injection-molded parts, making them suitable for functional components and end-use products.
High Precision and Detail:
Complex details and high-precision parts can be produced, making it suitable for industrial applications.
Variety of Material Options:
In addition to nylon, there are other materials such as glass-filled nylon and elastomers to meet various requirements.
Strong Mass Production Capability:
Large numbers of parts can be stacked and printed at once, improving production efficiency.
Cons
Higher Surface Roughness:
The printed surface often has a powdery texture and requires post-processing (such as sandblasting or polishing) to achieve a smooth finish.
High Equipment and Material Costs:
Initial investment and material costs are higher compared to other 3D printing technologies.
Limited Print Size:
The print size is constrained by the size of the equipment, and large parts may need to be printed in sections.
High Energy Consumption:
The laser sintering process consumes a significant amount of energy, increasing operational costs.
Complex Post-Processing:
Removing unsintered powder and performing subsequent surface treatment increases production time and costs.
Limited Color Options:
Materials are typically available in natural or basic colors, with fewer options for full-color printing.
SLS 3D Printing FAQs
1.What is SLS 3D Printing?
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a 3D printing technology that uses a laser to sinter powdered material, fusing it together to form solid structures. It is widely used for creating functional parts, prototypes, and complex geometries with high precision and strength.
2. What materials can be used in SLS 3D printing?
SLS 3D printing primarily uses powder-based materials such as:
Nylon (PA12, PA11)
Glass-filled Nylon
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
Aluminum
Steel
Polystyrene (PS)
These materials offer various mechanical properties like flexibility, strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability.
3. What are the advantages of SLS 3D printing?
No Support Structures: The powder itself supports the printed parts, allowing for complex geometries and internal cavities.
High Material Utilization: Unused powder can be reused, reducing waste and lowering material costs.
Strong Mechanical Properties: SLS parts have excellent strength and durability, suitable for functional components.
High Precision and Detail: Capable of printing intricate details with high accuracy.
Variety of Materials: A wide range of materials, including flexible and reinforced options, are available for different applications.
Scalable Production: Multiple parts can be printed simultaneously, improving production efficiency.
4. What are the limitations of SLS 3D printing?
Surface Roughness: Printed parts often have a rough surface finish due to powder particles, requiring post-processing (such as sandblasting or polishing) for a smoother finish.
Higher Costs: Initial investment in SLS machines and materials can be higher compared to other 3D printing methods.
Size Limitations: The maximum print size is constrained by the size of the printer. Larger parts may need to be split into multiple pieces.
Energy Consumption: SLS printing uses significant energy due to the high temperatures required for sintering.
Post-Processing Requirements: After printing, parts need to be cleaned to remove excess powder and may require additional surface treatment.
Limited Color Options: While functional, SLS materials are usually available in natural or basic colors, and full-color printing options are limited.
5. Can SLS 3D printing produce end-use parts?
Yes, SLS is ideal for producing end-use parts. Due to its strong mechanical properties and material options (such as glass-filled nylon or aluminum), it is commonly used in industries like aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer products for producing durable, functional components.
6.How does post-processing work in SLS 3D printing?
After printing, the parts are removed from the build platform, and excess powder is removed using air pressure or a brushing method. Depending on the material, additional post-processing steps such as sanding, polishing, or dyeing may be required to improve surface finish, strength, or appearance.
7.Can SLS print complex geometries?
Yes, one of the key benefits of SLS 3D printing is its ability to print highly complex and intricate geometries, including internal cavities and overhangs, without the need for support structures.
8. What industries commonly use SLS 3D printing?
SLS 3D printing is widely used across many industries:
Aerospace: For lightweight, durable parts with complex shapes.
Automotive: For prototyping, low-volume production, and functional parts.
Medical: For custom prosthetics, implants, and surgical tools.
Consumer Products: For producing functional prototypes and end-use products.
Engineering: For low-volume production of industrial parts, tools, and fixtures.
9. How do I ensure high-quality SLS prints?
To achieve the best quality prints, ensure the following:
Material Quality: Use high-quality, well-maintained materials.
Printer Calibration: Ensure the printer is properly calibrated for consistent results.
Post-Processing: Adequately post-process your prints to achieve the desired finish and properties.
10. How long does an SLS print take?
The print time for SLS 3D printing depends on factors like part size, complexity, and material used. Generally, prints can take anywhere from a few hours to several days, especially for large or detailed parts.
Other 3D Printing Capabilities from ProtoTi

SLA
Stereolithography
- Visual part prototyping. High resolution. Low cost.
- Dimensional accuracy of ±0.2% with a lower limit of ±0.2mm.
- Lead times from 2 business days

SLS
Selective Laser Sintering
- Functional prototyping. Low-run production.
- Dimensional accuracy of ±0.3% with a lower limit of ±0.3mm.
- Lead times from 3 business days

MJF
Multi Jet Fusion
- Functional prototyping. Low-run production.
- Dimensional accuracy of ±0.3% with a lower limit of ±0.3mm.
- Lead times from 3 business days

SLM
Selective Laser Melting
- Metal parts rapid prototyping. Production grade.
- Dimensional accuracy of ±0.2% with a lower limit of ±0.2mm.
- Lead times from 4 business days

FDM
Fused Deposition Modeling
- Plastic parts rapid prototyping. Low cost.
- Dimensional accuracy of ±0.2% with a lower limit of ±0.2mm.
- Lead times from 4 business days

DLP
Digital Light Processing
- Resin parts rapid prototyping. High details.
- Dimensional accuracy of ±0.2% with a lower limit of ±0.2mm.
- Lead times from 4 business days

