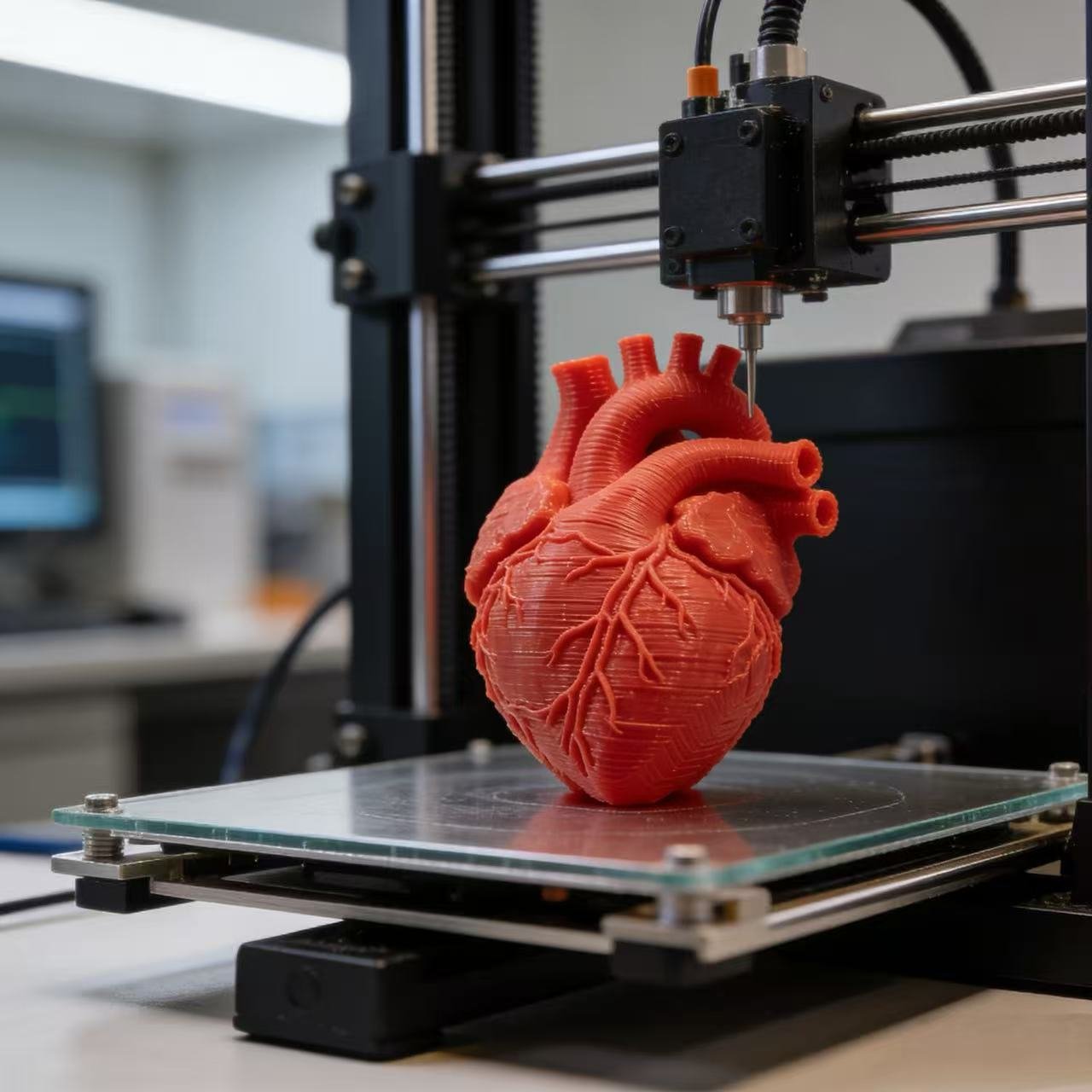
How 3D Printing Saved a Baby’s Life: A Groundbreaking Medical Case
In the high-stakes world of pediatric cardiology, surgeons often operate with limited information, navigating tiny, complex, and uniquely malformed hearts.
Dear Valued Customer,
Thank you sincerely for your continued trust and support throughout the year 🙏
As the Chinese New Year approaches, order volumes naturally increase as we prepare for the holiday season.
For our team in China, the Chinese New Year is the most important time of the year—a moment after months of hard work to reunite with family and celebrate together 🧧🏮. We truly appreciate your understanding and support during this special period.
To help you plan ahead, please find our shipping arrangements below:
Orders placed before February 1st will be shipped by the cut-off date of February 11th.
Orders placed between February 2nd and February 4th may still be shipped before February 11th, depending on production capacity.
Orders placed on or after February 5th will require extended lead time and will be shipped gradually starting February 24th.
Please note that most manufacturers in China, including ProtoTi, will pause production from February 10th to February 23rd for the Chinese New Year holiday.
If the potential delay does not fit your schedule, please let us know as soon as possible. We will be happy to assist with a refund, provided the order has not yet entered production.
Once again, thank you for your understanding and for being a valued partner of ProtoTi. For any delayed orders, we will proactively provide individual updates with confirmed delivery timelines.
On behalf of the entire ProtoTi Global Business Team, we wish you and your family a joyful, healthy, and prosperous New Year 🎉✨
Warm regards,
ProtoTi Global Business Team


304 stainless steel is one of the most commonly used austenitic stainless steels and belongs to the 18-8 stainless steel series. Its main chemical components are approximately 18% chromium (Cr) and 8% nickel (Ni), giving it excellent corrosion resistance and processing performance. Due to its superior properties, 304 stainless steel is widely used in construction, kitchenware, medical instruments, and food processing equipment.
The corrosion resistance of stainless steel 304 is one of its core competitiveness. Due to the chromium element forming a dense chromium oxide passivation film on the surface of the steel, this film can isolate air, moisture and various corrosive media, preventing the internal steel from oxidation and erosion. In natural environments, 304 stainless steel can maintain a smooth surface for a long time and is not easy to rust; in weak corrosive environments, such as fresh water, neutral salt solutions, and organic acids at room temperature, its corrosion resistance also performs excellently.
It should be noted that stainless steel 304 is not absolutely rust-proof, and its corrosion resistance is closely related to the service environment. In strong corrosive environments, such as high-concentration chloride ion solutions and strong acid-base environments, the passivation film may be damaged, leading to steel rust. Therefore, when used in special environments, it is necessary to select higher-grade stainless steel (such as 316L) or take anti-corrosion measures according to the working conditions.
Stainless steel 304 has good strength, hardness and toughness. Its tensile strength can reach 515-655MPa, yield strength ≥205MPa, and elongation ≥40%. This balanced mechanical performance enables it to withstand a certain degree of impact load and pressure, making it suitable for manufacturing structural parts, mechanical parts and other components that need to bear external forces.
At the same time, 304 stainless steel has excellent toughness. Even in low-temperature environments (such as -270℃), it can maintain good toughness without brittle fracture, so it can be used in the manufacture of low-temperature equipment.

Stainless steel 304 is easy to perform various processing treatments, including stamping, bending, shearing, welding, turning, milling, etc. It has excellent welding performance and can adopt various welding methods such as arc welding, argon arc welding, and gas shielded welding. After welding, the joint has high strength and stable performance, without the need for complex post-welding treatment.
In addition, 304 stainless steel can also undergo surface treatments such as polishing, pickling and passivation, sandblasting, etc., to meet the appearance and usage requirements of different scenarios.
The heat resistance temperature of stainless steel 304 can reach 870℃. In high-temperature environments, it can still maintain good mechanical performance and stability without obvious deformation or performance degradation. Therefore, it is often used in the manufacture of equipment and parts under high-temperature working conditions, such as boilers, heat exchangers, oven liners, exhaust pipes, etc.
When the continuous service temperature does not exceed 870℃ and the intermittent service temperature does not exceed 925℃, 304 stainless steel can work stably, making it an ideal choice for heat-resistant stainless steel in the medium and low-temperature fields.
Stainless steel 304 does not contain harmful substances such as lead and mercury, and has a smooth surface that is not easy to breed bacteria. After passing food-grade certification, it can be used in the manufacture of food processing, storage and transportation equipment, such as stainless steel tableware, kitchen utensils, food machinery, drinking water pipes, etc.
Its non-toxic and environmentally friendly characteristics have also made it widely used in medical, health and other fields, such as medical devices, hospital cleanroom equipment, etc.
| Element | Content Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cr | 18-20% | Enhances corrosion resistance |
| Ni | 8-10.5% | Improves toughness and corrosion resistance |
| C | ≤0.08% | Controls hardness and weldability |
| Mn | ≤2% | Improves strength and oxidation resistance |
| Si | ≤1% | Improves heat resistance |
| P | ≤0.045% | Reduces brittleness |
| S | ≤0.03% | Improves machinability |
| Property | Value | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.93 | g/cm³ | Material mass density |
| Melting Point | 1400–1450 | °C | Melting range |
| Thermal Conductivity | 16.2 | W/m·K | Thermal conductivity |
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.73 | μΩ·m | Electrical resistivity at 20°C |
| Property | Value | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 520–750 | MPa | Ability to resist tensile forces |
| Yield Strength | 205 | MPa | Stress at yield point |
| Elongation | 40 | % | Percentage elongation before fracture |
| Hardness | 70–90 | HRB | Resistance to indentation and wear |
Hot-Rolled Sheet:Thickness >2 mm, rough surface, suitable for industrial structures.
Cold-Rolled Sheet:Thickness <2 mm, smooth surface, suitable for decorative purposes.
Brushed Surface:Decorative finish
Mirror Finish:Bright reflective finish
Matte Finish:Non-slip, wear-resistant
| Type | Size Range | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Sheet | 0.3 – 100 mm in thickness | Construction, kitchenware, machinery plates |
| Tube | Outer diameter: 6 – 630 mm | Piping, structural support, decoration |
| Profile | Angle steel, round steel, special-shaped materials | Mechanical structures, brackets, frames |
Correct heat treatment is key to ensuring the performance of 304 stainless steel:
Annealing: Heating the material to 1040-1120°C, holding, and then rapidly cooling (water quenching or air cooling). This process dissolves carbides, eliminates work hardening, restores corrosion resistance, and achieves a uniform austenitic structure.
Stress Relieving: For components that need to reduce residual stress after cold working without significantly reducing strength, low-temperature annealing can be performed at 400-500°C.
Precautions:
Avoid staying for a long time within the “sensitization range” of 450 – 850℃.
Remove scale after heat treatment (pickling, sandblasting, or mechanical polishing).
Keep the surface clean to avoid carburization.
304 stainless steel has good formability, but requires more attention compared to carbon steel:
Due to significant work hardening, complex forming may require intermediate annealing.
Springback is about 1.5-2 times greater than carbon steel; mold design must account for compensation.
Compared to carbon steel, greater forming force and more wear-resistant mold materials are required.
Conducted within the temperature range of 1150-1260°C. Avoid significant deformation below 900°C, as it can lead to undesirable microstructure and properties.
The limiting drawing ratio of 304 stainless steel is approximately 2.0-2.2, which is better than most steels. Using high-lubricity media (e.g., lubricating oils with extreme pressure additives) can improve the forming limit.
Suitable for all conventional welding methods (TIG, MIG, resistance welding, etc.)
It is recommended to use low-carbon grades (304L) or niobium-stabilized grades to avoid intergranular corrosion in the weld zone.
Matching or over-matching filler metals (e.g., 308L).
Control heat input to avoid overheating.
Post-weld heat treatment is usually not required.
Pay attention during threaded connections, riveting, and fastening:
Avoid galvanic corrosion caused by direct contact with other metals.
Use appropriate gaskets or coatings for isolation.
Control tightening torque to avoid over-tightening, which can lead to stress corrosion risk.
Surface treatments can not only enhance aesthetics but also improve functional performance:
Mechanical Polishing: Achieves mirror or various texture finishes but may introduce surface residual stresses.
Electropolishing: Removes the surface layer through an electrochemical process, resulting in a smooth, clean surface while improving corrosion resistance.
Passivation: Uses nitric or citric acid solutions to enhance the passive film, improving corrosion resistance, especially after removing surface iron contamination.
Coloring: Produces interference films through chemical or electrochemical methods to achieve various colors (but 304 stainless steel is not as easy to color as grades with higher chromium content).
In the field of architectural decoration, stainless steel 304 has become a popular material due to its beautiful appearance, durability and easy cleaning. Common applications include:
Exterior wall decoration: 304 stainless steel plates can be used for curtain walls and decorative panels of building exterior walls. After polishing or brushing treatment, they show a simple and elegant metal texture, and have strong weather resistance, not easy to fade or rust after long-term use;
Interior decoration: Used for stair handrails, railings, door and window frames, ceiling decorations, skirting lines, etc., which can not only improve the grade of the space but also facilitate daily cleaning and maintenance;
Machinery manufacturing: Used for manufacturing casings, components, transmission parts of mechanical equipment, such as machine tools, water pumps, valves, bearing seats, etc. Its good mechanical performance and corrosion resistance can ensure the long-term stable operation of the equipment;
Chemical equipment: Suitable for manufacturing chemical pipelines, storage tanks, reactors, heat exchangers, etc., which can withstand the corrosion of most organic and inorganic chemicals, ensuring the safe and efficient chemical production;
Food industry: Food-grade 304 stainless steel is widely used in the manufacture of food processing machinery (such as mixers, slicers, conveyor lines), food storage equipment (such as storage tanks, shelves), tableware (such as stainless steel pots, bowls, ladles, basins), drinking water pipes, etc., to ensure the safety and hygiene of food during processing and storage;
Medical industry: Used for manufacturing medical devices (such as surgical instruments, syringes, infusion sets), hospital beds, medical carts, cleanroom wall and floor materials, etc. Its non-toxic, corrosion-resistant and easy-to-sterilize characteristics meet the strict hygiene requirements of the medical industry.
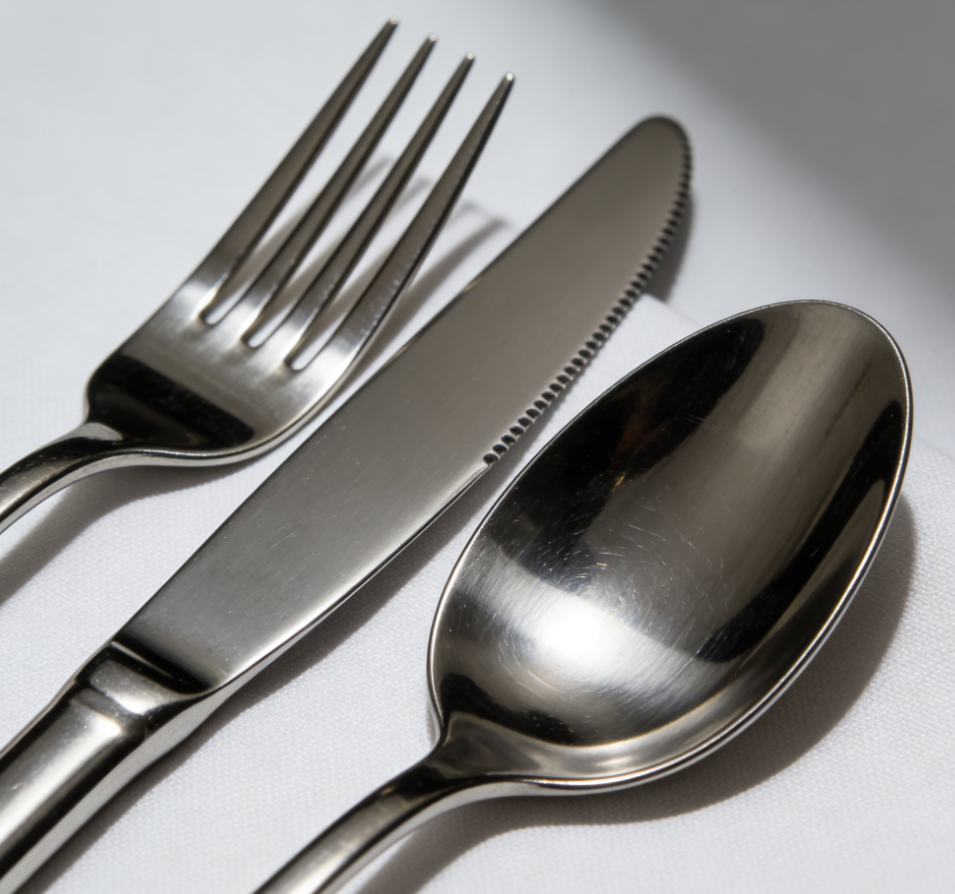
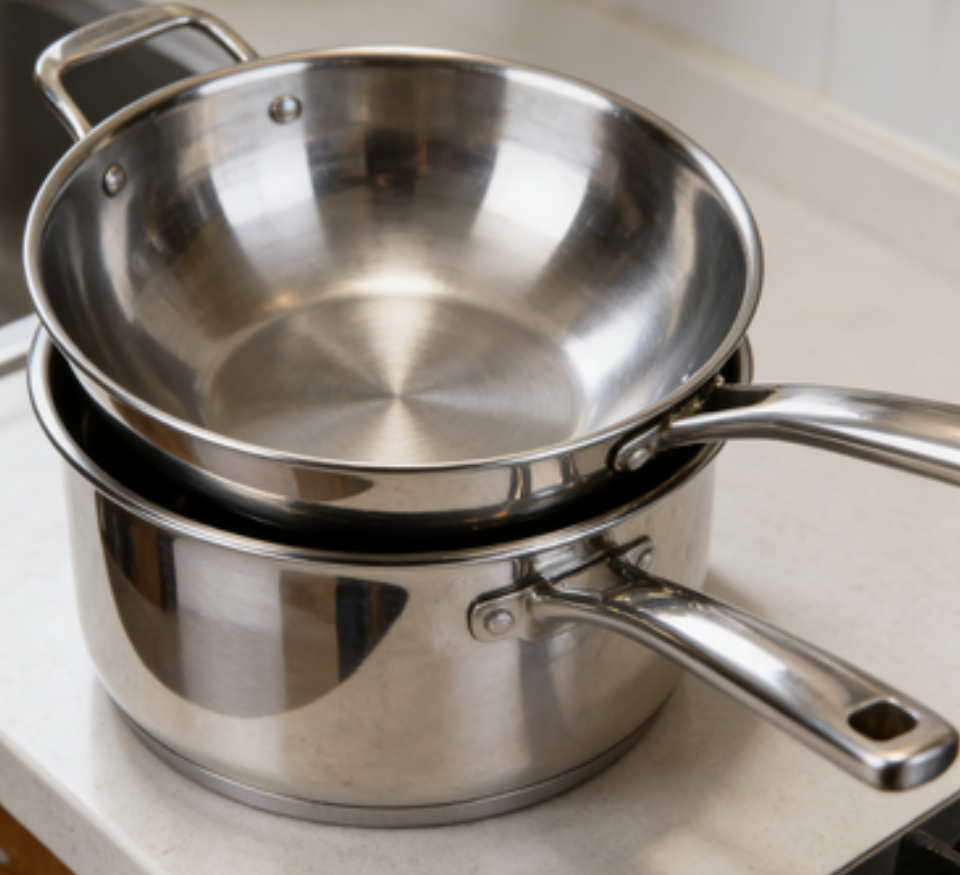


Household items: Stainless steel tableware, kitchen utensils, thermos cups, kettles, clothes drying racks, towel racks, bathroom storage racks, etc., are durable, easy to clean and not easy to rust, and are essential items for home life;
Home appliances: Some components of home appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, microwave ovens, dishwashers, such as refrigerator inner tanks, washing machine inner barrels, air conditioner heat exchangers, etc., using 304 stainless steel material can improve the durability and hygiene of the products;
Since its introduction in the early 20th century, 304 stainless steel has proven its enduring value as a versatile engineering material. It balances performance, workability, aesthetics, and cost-effectiveness, becoming a foundational material for numerous industries. Although new materials continue to emerge, 304 stainless steel, with its mature processes, reliable data support, and extensive application experience, will maintain an important position in the foreseeable future.
For engineers and designers, fully understanding the performance boundaries and correct application conditions of 304 stainless steel is key to achieving optimal design. For consumers and users, recognizing the characteristics and maintenance requirements of this material can ensure its long-term performance and value.
In today’s pursuit of sustainable development and a circular economy, the full life cycle advantages of 304 stainless steel are even more prominent. It is not only a pillar material of modern industry but also an important bridge connecting the present and the future. With technological progress and application innovation, this classic alloy will undoubtedly continue to evolve, creating a safer, healthier, and more sustainable living environment for humanity.

Start your project today. Get free DFM from professional engineer at ProtoTi.
Share the Post:

In the high-stakes world of pediatric cardiology, surgeons often operate with limited information, navigating tiny, complex, and uniquely malformed hearts.

Saab AB and Divergent Technologies have completed a fully additively manufactured aircraft fuselage measuring five meters in length, built using

Justin Bieber’s fashion label Skylrk is expanding into 3D printed footwear with its first printed sneaker, the Earth Bender, developed
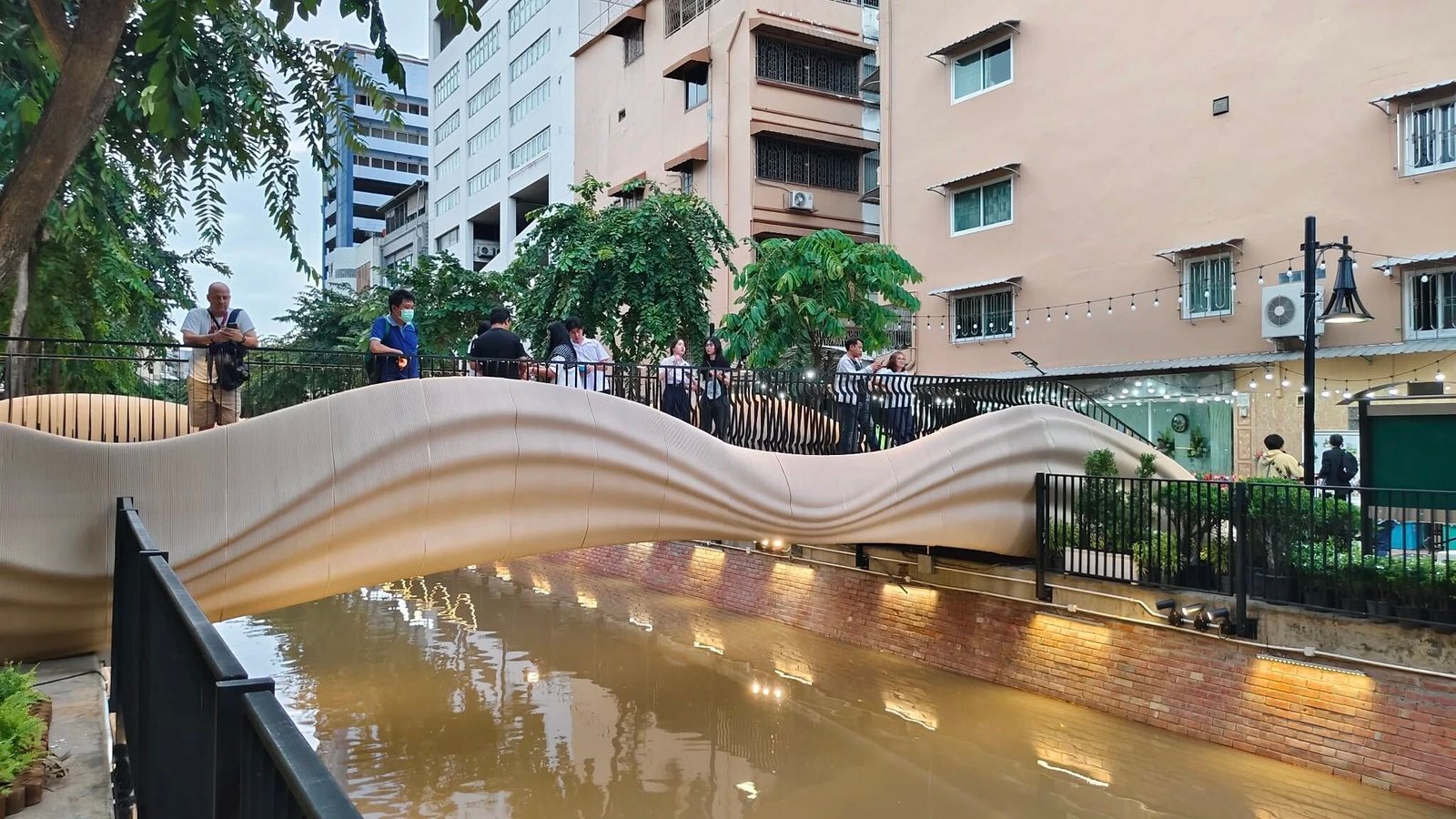

Thai Siam Cement Group (SCG) has delivered a 3D printed pedestrian bridge across Bangkok’s historic Ong Ang Canal, marking one