
Fraunhofer ILT Tests 3D Printed Titanium Reactors to Generate Hydrogen Onboard Heavy Vehicles
The Aachen-based Fraunhofer Institute for Laser Technology (Fraunhofer ILT) is to research titanium aluminide hydrogen reactors and heat exchangers. The
🌸With the arrival of spring, our company has officially resumed full operation and production capacity after the Spring Festival holiday. We sincerely thank all customers for your patience and support.
To honor International Women’s Day and thank you for your trust, we are launching a limited-time special promotion:
⏰ Promotion Time
March 5 – March 31
🎯 Exclusive Discount
8% OFF Coupon for all orders placed during the valid period.
💡 Warm Tips
Place your order early to enjoy priority production and guaranteed delivery time.
This event is dedicated to celebrating the power of women worldwide and thanking you for your continued partnership.
For any inquiries, please contact our sales team.
Thank you for choosing us, and let’s move forward to a prosperous new year together!
Best regards,
ProtoTi Global Business Team


Next, let’s explore the key components of the 3D-printed rocket and the manufacturing process for them.
3D printing enables the creation of complex rocket parts that were previously impossible or costly to produce with traditional methods. Critical components such as engine nozzles, fuel injectors, and combustion chambers can be printed as single pieces, eliminating the need for assembly and reducing the risk of failure. Metal alloys like titanium and nickel-based superalloys are commonly used, offering high strength and heat resistance essential for space travel.
The process begins with a digital 3D model, which is sliced into thin layers. A 3D printer then deposits material layer by layer, fusing each layer to build the final part. This additive approach minimizes material waste and allows for rapid prototyping and iteration.
The German Aerospace Center (DLR) collaborated with the Customer Innovation Center (CIC) of 3D Systems and achieved a breakthrough in the innovation of rocket engine fuel injectors through metal 3D printing technology in 2018.
Terran 1 conducted the world’s first fully 3D-printed rocket launch in March 2023 (with 95% of the components being printed), although it did not reach orbit, it verified the reliability of the 3D-printed structure.
The Terran R project is scheduled to make its maiden flight in 2026, with a focus on reusable technology (capable of transporting 20 tons in Low Earth Orbit).
3D printing is accelerating the advancement of space exploration at an unprecedented pace. Its application in rocket manufacturing not only enhances reliability but also greatly expands design possibilities, ushering in a new chapter for humanity’s journey into deeper space.

Share the Post:

The Aachen-based Fraunhofer Institute for Laser Technology (Fraunhofer ILT) is to research titanium aluminide hydrogen reactors and heat exchangers. The

Step into a modern kitchen, open a refrigerator, walk into an office building elevator, or observe medical equipment—in these seemingly different scenarios, one material silently underpins our lives: Stainless Steel 304. As the most common and widely used grade of austenitic stainless steel, SS304 has become an “invisible champion” in industrial manufacturing and daily life, thanks to its excellent corrosion resistance, good formability, and outstanding hygienic properties.
Since stainless steel was invented in the early 20th century, 304 stainless steel has evolved into the world’s most popular stainless steel variety, accounting for approximately 50% of the stainless steel market share. From aerospace to food processing, from architectural decoration to medical devices, this alloy occupies an irreplaceable position in modern materials science due to its unique combination of properties. This article will provide a comprehensive analysis of the chemical composition, mechanical properties, application fields, processing techniques, and selection guidelines for 304 stainless steel, offering a thorough reference for engineers, designers, purchasers, and general consumers.
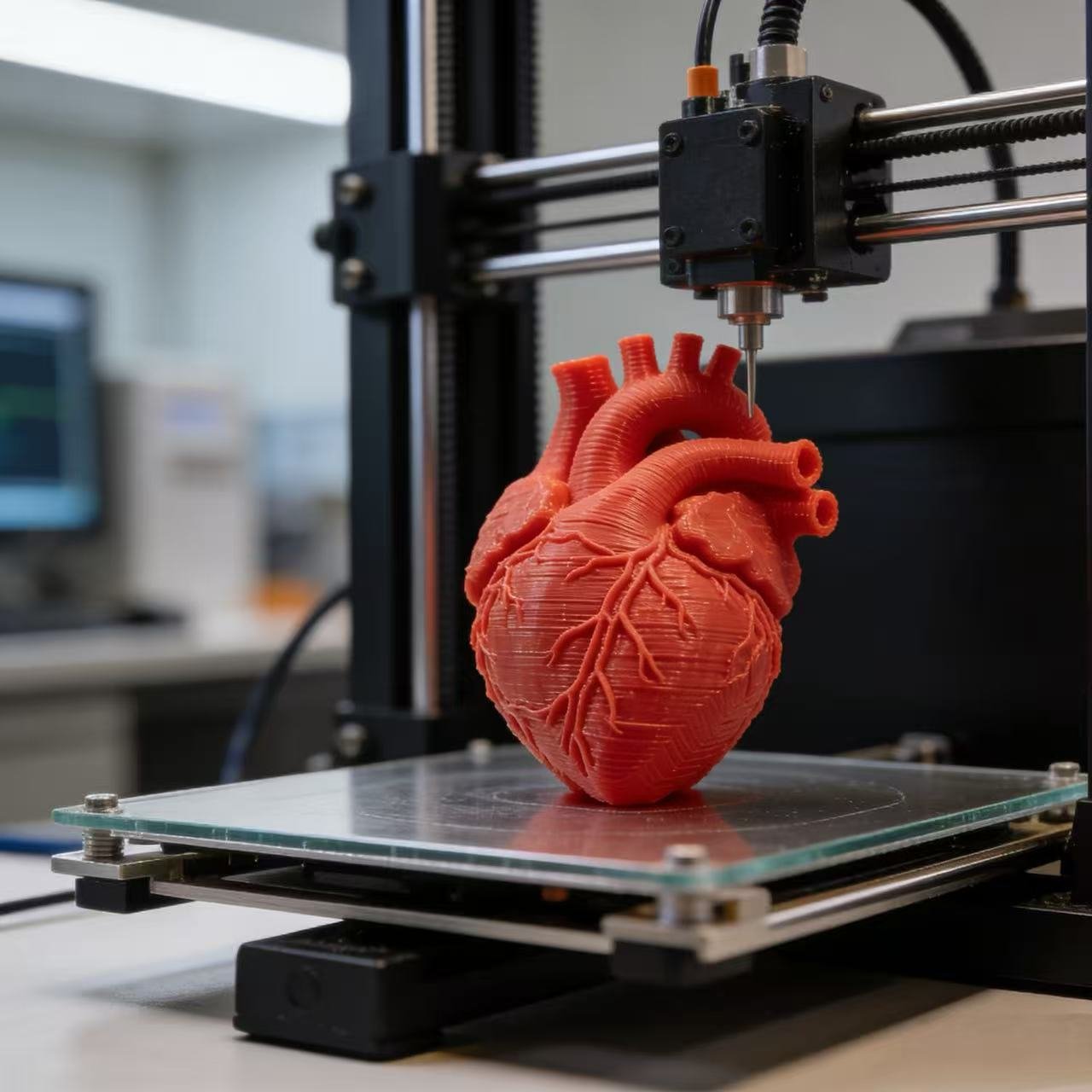
In the high-stakes world of pediatric cardiology, surgeons often operate with limited information, navigating tiny, complex, and uniquely malformed hearts.

Saab AB and Divergent Technologies have completed a fully additively manufactured aircraft fuselage measuring five meters in length, built using